To decrease inflammation use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Plantain
Genus and Species Name: Plantago lanceolata
Habitat: Fields, waste places, and yards
Seasons: Spring-fall
Medicinal uses: The leaves of the plantain are used to make a poultice. It contains aucubin which is an iridoid, that reduces inflammation.
Preparation: Take the plantain leaf and chew on it. Then, the chewed up leaf can be directly applied or put in a thin cloth and applied or taped to the bite area. This will decrease inflammation.
Active Chemical Ingredient: aucubin
Chemical Formula: C15H22O9
Chemical Structure:
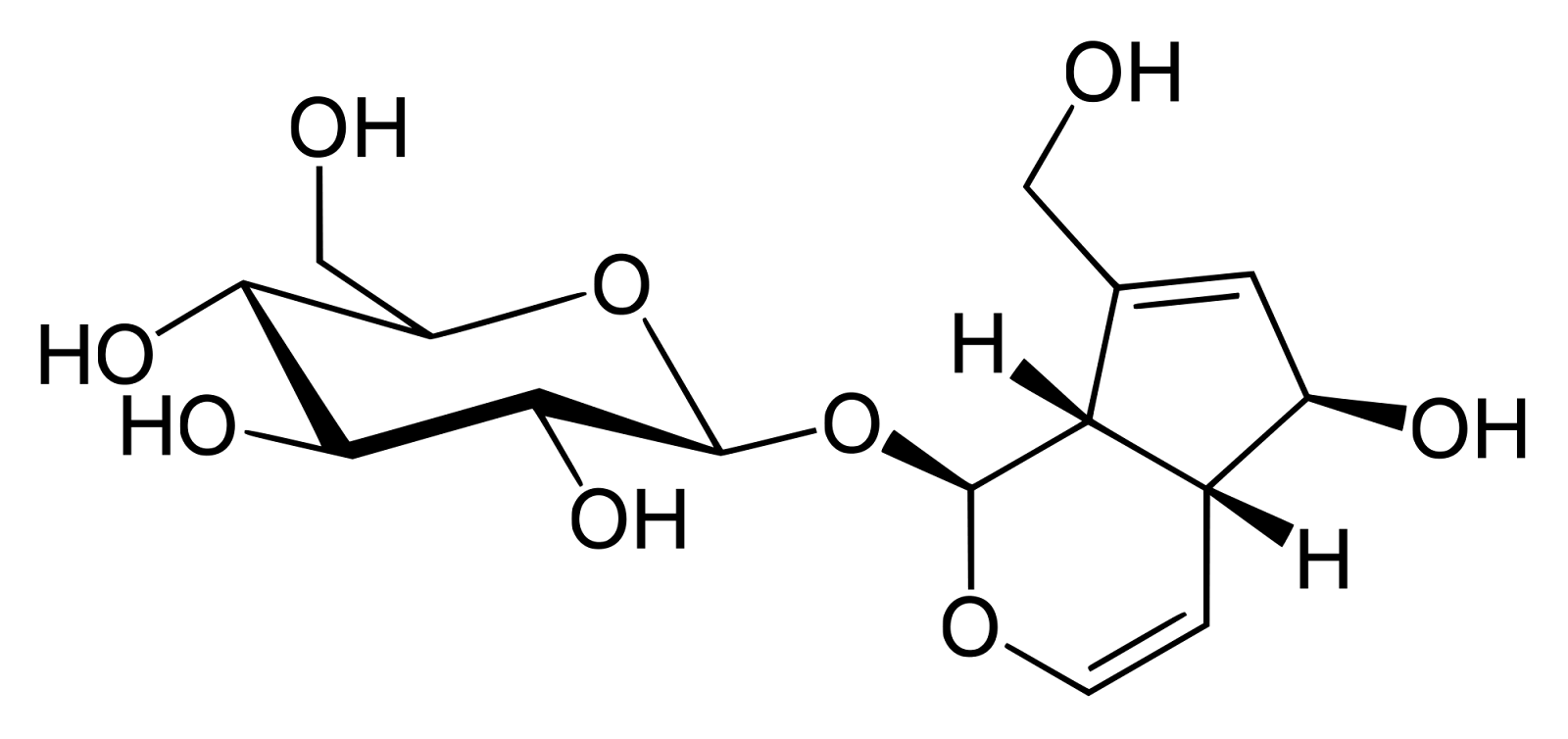
Habitat: Fields, waste places, and yards
Seasons: Spring-fall
Medicinal uses: The leaves of the plantain are used to make a poultice. It contains aucubin which is an iridoid, that reduces inflammation.
Active Chemical Ingredient: aucubin
Chemical Structure:
Resources:
INSECT BITE REMEDIES THAT REALLY WORK AND STOP THE ITCH! (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.healing-from-home-remedies.com/insect-bite-remedies.html
English Plantain. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/english-plantain
Plantago major - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/plantago-major.html(n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aucubin
Viljoen, A., Mncwangi, N., & Vermaak, I. (n.d.). Anti-Inflammatory Iridoids of Botanical Origin. Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3873812/
Result Filters. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22822679
To fight infection use:
Plantago major - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/plantago-major.html(n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aucubin
Viljoen, A., Mncwangi, N., & Vermaak, I. (n.d.). Anti-Inflammatory Iridoids of Botanical Origin. Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3873812/Result Filters. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22822679
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Wild onion
Genus and Species Name: Allium stellatum
Habitat: Meadows, swamps, fields, and openings of dry upland forests.
Habitat: Meadows, swamps, fields, and openings of dry upland forests.
Seasons: Early spring- fall (perennial)
Medicinal uses: The onion is eaten because it contains quercetin, which are anti-bacterial.
Preparation: Harvest onion plants, wash, and eat to kill bacteria in stomach.
Active Chemical Ingredient: quercetin
Seasons: Early spring- fall (perennial)
Medicinal uses: The onion is eaten because it contains quercetin, which are anti-bacterial.
Active Chemical Ingredient: quercetin
Chemical Formula: C15H10O7
Chemical Structure:
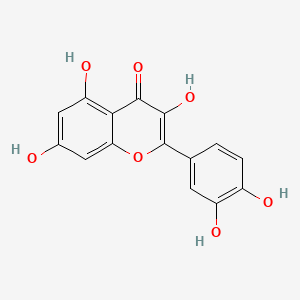
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
The onion plant kills E. coli bacteria. (2013, October 9). Retrieved September 9, 2015, from http://www.naturalhealth365.com/food_news/onion_bacteria.html
Allium cepa - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 9, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/allium-cepa.html
Quercetin. (n.d.). Retrieved September 9, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/quercetin#section=2D-Structure
Wild Onion (Wild Pink Onion). (n.d.). Retrieved September 9, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/wild-onion-wild-pink-onion
Nyerges, C. (n.d.). Guide to Wild Foods and Useful Plants (p. 188,189).
Bown, D. (n.d.). Encyclopedia of Herbs and Their Uses (p. 234).
Nyerges, C. (n.d.). Guide to Wild Foods and Useful Plants (p. 188,189).
Bown, D. (n.d.). Encyclopedia of Herbs and Their Uses (p. 234).


No comments:
Post a Comment