To treat pain use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Purple coneflower
Genus and Species Name: Echinacea purpurea
Habitat: Prairies, roadsides, pastures, and openings in moist woods
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
Preparation: The crushed roots (with a mortar and pestle) are mixed in a 1:2 ratio with alcohol. After letting the combined material sit for several weeks, strain and store in a dark bottle (so sunlight does not degrade it). The tincture can be taken by mouth directly or diluted in water.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Formula: C35H46O20
Chemical Structure:
 Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
Habitat: Prairies, roadsides, pastures, and openings in moist woods
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
To reduce swelling use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Soapweed yucca
Genus and Species Name: Yucca glauca and Yucca arkansana
Habitat: Glades, open rocky woods, and roadsides, and loess hill prairies
Seasons: Yucca roots are available year round (perennial).
Medicinal uses: Use yucca roots in a steam bath to relieve pain.
Preparation: First, pulverize the yucca roots and place them in water. Boil the water until there is steam. Place the sprained body part over the steam bath to relieve pain.
Active Chemical Ingredient: tannin
Chemical Formula: C76H52O46
Seasons: Yucca roots are available year round (perennial).
Medicinal uses: Use yucca roots in a steam bath to relieve pain.
Active Chemical Ingredient: tannin
Chemical Structure:
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
Yuccas (Spanish Bayonet; Soapweed; Adam's Needle). (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/yuccas-spanish-bayonet-soapweed-adam-s-needle
NPIN: Native Plant Database. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=YUGL
Investigation. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://tolweb.org/treehouses/?treehouse_id=4591
Chevallier, A., & Keifer, D. (2010). Herbal remedies. New York: Metro Books.
(n.d.). Retrieved September 7, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tannin
Resources:
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).Yuccas (Spanish Bayonet; Soapweed; Adam's Needle). (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/yuccas-spanish-bayonet-soapweed-adam-s-needle
NPIN: Native Plant Database. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=YUGL
Investigation. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://tolweb.org/treehouses/?treehouse_id=4591
Chevallier, A., & Keifer, D. (2010). Herbal remedies. New York: Metro Books.
(n.d.). Retrieved September 7, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tannin
To also reduce swelling use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Sassafras
Genus and Species Name: Sassafras albidum
Habitat: Pastures, roadsides, thickets, and on the border of dry woods
Seasons: Sassafras root is available year round.
Medicinal uses: The sassafras oil is an antiseptic (kills germs) and analgesic (pain killer). It also reduces swelling (anti- inflammatory).
Preparation: The sassafras root is boiled in order to extract its oil. Oil is lighter than water, so it will separate. Then one can remove the oil from the water and apply it to the skin in order to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and kill germs.
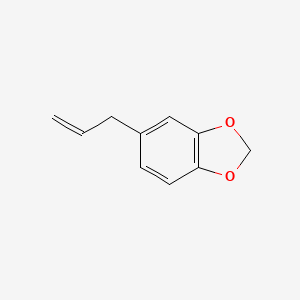
Active Chemical Ingredient: Safrole
Chemical Formula: C10H10O2
Chemical Structure:
Habitat: Pastures, roadsides, thickets, and on the border of dry woods
Seasons: Sassafras root is available year round.
Medicinal uses: The sassafras oil is an antiseptic (kills germs) and analgesic (pain killer). It also reduces swelling (anti- inflammatory).
Preparation: The sassafras root is boiled in order to extract its oil. Oil is lighter than water, so it will separate. Then one can remove the oil from the water and apply it to the skin in order to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and kill germs.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Safrole
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Safrole. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/safrole#section=Top
Medical Attributes of Sassafras albidum - sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://klemow.wilkes.edu/Sassafras.html
Sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/sassafras
Sassafras albidum - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/sassafras-albidum.html
Ayers, C. (n.d.). How to Extract Sassafras Oil. Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.ehow.com/how_7766393_extract-sassafras-oil.html
Resources:
Safrole. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/safrole#section=TopMedical Attributes of Sassafras albidum - sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://klemow.wilkes.edu/Sassafras.html
Sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/sassafras
Sassafras albidum - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/sassafras-albidum.html
Ayers, C. (n.d.). How to Extract Sassafras Oil. Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.ehow.com/how_7766393_extract-sassafras-oil.html
*In addtion, use limbs and fabric (or rope made from woven yucca fibers) to make a splint to keep the broken bone in place to prevent further damage and more pain.
*In addtion, use limbs and fabric (or rope made from woven yucca fibers) to make a splint to keep the broken bone in place to prevent further damage and more pain.



No comments:
Post a Comment