To reduce inflammation use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest
Common Name: American ash
Genus and Species Name: Fraxinus americana
Habitat: Forests along streams and bluffs
Habitat: Forests along streams and bluffs
Seasons: Bark is available year-round.
Medicinal uses: The inner bark of the ash tree is used to reduce inflammation.
Preparation: The inner bark of the ash tree is chewed and used as a poultice to the snake bite sore.
Active Chemical Ingredient: betulin
Seasons: Bark is available year-round.
Medicinal uses: The inner bark of the ash tree is used to reduce inflammation.
Active Chemical Ingredient: betulin
Chemical Formula: C30H50O2
Chemical Structure:

Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Fraxinus americana - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/fraxinus-americana.html
(n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betulin
White Ash. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/white-ash
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
Resources:
Fraxinus americana - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/fraxinus-americana.html
(n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betulin
White Ash. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/white-ash
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
(n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betulin
White Ash. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/white-ash
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Goldenrod
Genus and Species Name: Solidago gigantea
Habitat: Prairies, openings in woods with sun, and meadows
Habitat: Prairies, openings in woods with sun, and meadows
Seasons: flowers bloom June-December
Medicinal uses: Dried goldenrod flowers are used to reduce inflammation.
Preparation: Steep 1-2 tsp. of the dried goldenrod flowers in a cup of hot water for 10 minutes. Then, drink the tea to reduce inflammation.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Leiocarposide
Seasons: flowers bloom June-December
Medicinal uses: Dried goldenrod flowers are used to reduce inflammation.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Leiocarposide
Chemical Formula: C27H34O16
Chemical Structure:
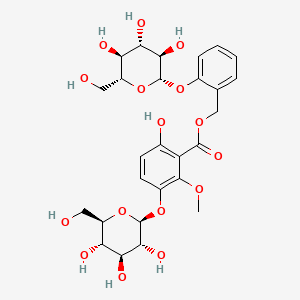
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
(n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/goldenrods
Solidago gigantea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/solidago-gigantea.html
Solidago drummondii - Plant Finder. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=y410
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
Goldenrod. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.altmd.com/Articles/Goldenrod--Encyclopedia-of-Alternative-Medicine
Leiocarposide. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Leiocarposide
Goldenrod. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.altmd.com/Articles/Goldenrod--Encyclopedia-of-Alternative-Medicine
To treat pain use:
Resources:
(n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/goldenrodsSolidago gigantea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/solidago-gigantea.html
Solidago drummondii - Plant Finder. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=y410
Foster, S., & Duke, J. (n.d.). Peterson field guide to medicinal plants and herbs of eastern and central North America (Third ed.).
Goldenrod. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.altmd.com/Articles/Goldenrod--Encyclopedia-of-Alternative-Medicine
Leiocarposide. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Leiocarposide
Goldenrod. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.altmd.com/Articles/Goldenrod--Encyclopedia-of-Alternative-Medicine
To treat pain use:
Eastern Dediduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Purple coneflower
Genus and Species Name: Echinacea purpurea
Habitat: Prairies, roadsides, pastures, and openings in moist woods
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
Preparation: The crushed roots (with a mortar and pestle) are mixed in a 1:2 ratio with alcohol. After letting the combined material sit for several weeks, strain and store in a dark bottle (so sunlight does not degrade it). The tincture can be taken by mouth directly or diluted in water.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Formula: C35H46O20
Chemical Structure:
 Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
Habitat: Prairies, roadsides, pastures, and openings in moist woods
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower



No comments:
Post a Comment