To treat pain use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest
Common Name: River Birch
Genus and Species Name: Betula nigra
Habitat: Wooded areas along creeks or rivers
Seasons: Leaves grow spring-fall.
Medicinal uses: River birch leaves are used make a tea that treat pain. The leaves contain methyl salicylate, which acts like aspirin.
Preparation: A tea can be made by adding 2 tbsp. or birch bark and 1 tbsp. of wild ginger to hot water.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: methyl salicylate
Chemical Formula: C₈H₈O₃
Chemical Structure:
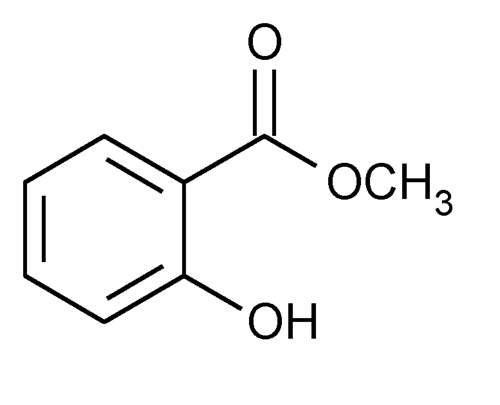
Resources:
Habitat: Wooded areas along creeks or rivers
Seasons: Leaves grow spring-fall.
Medicinal uses: River birch leaves are used make a tea that treat pain. The leaves contain methyl salicylate, which acts like aspirin.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: methyl salicylate
Chemical Structure:
NF Monographs: Methyl Salicylate. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.pharmacopeia.cn/v29240/usp29nf24s0_m52100.html
Birch Bark Tea With Ginger. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.anniesremedy.com/chart_remedy.php?rem_ID=702
Birches. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.eattheweeds.com/birches/
River Birch. (n.d.). Retrieved September 10, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/river-birch
Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Purple coneflower
Genus and Species Name: Echinacea purpurea
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
Preparation: The crushed roots (with a mortar and pestle) are mixed in a 1:2 ratio with alcohol. After letting the combined material sit for several weeks, strain and store in a dark bottle (so sunlight does not degrade it). The tincture can be taken by mouth directly or diluted in water.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Formula: C35H46O20
Chemical Structure:
 Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3
Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
To treat swelling and infection use:
Seasons: Blooms May- October
Medicinal uses: The purple coneflower's roots are used to make a tincture to relieve pain.
In addition, put the frostbit part of the body in cold water. Then, gradually increase the heat until it is warm.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Echinacoside
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Echinacea:The Art of Tincturing. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.motherearthliving.com/plant-profile/echinacea-the-art-of-tincturing.aspx?PageId=3Echinacoside. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.lktlabs.com/products/Echinacoside-2485-101.html
Echinacea purpurea - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/echinacea-purpurea.html
Purple Coneflower. (n.d.). Retrieved September 6, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/purple-coneflower
To treat swelling and infection use:
Eastern Deciduous Forest and Tall Grass Prairie
Common Name: Sassafras
Genus and Species Name: Sassafras albidum
Habitat: Pastures, roadsides, thickets, and on the border of dry woods
Seasons: Sassafras roots is available year round.
Medicinal uses: The sassafras oil is an antiseptic (kills germs) and analgesic (pain killer). It also reduces swelling.
Preparation: The sassafras root is boiled in order to extract its oil. Oil is lighter than water, so it will separate. Then one can remove the oil from the water and apply it to the blisters in order to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and kill germs.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Safrole
Chemical Formula: C10H10O2
Chemical Structure:
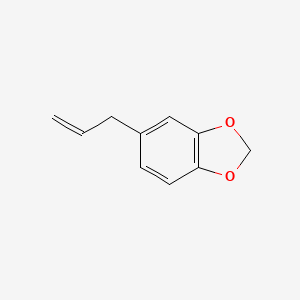
Habitat: Pastures, roadsides, thickets, and on the border of dry woods
Seasons: Sassafras roots is available year round.
Medicinal uses: The sassafras oil is an antiseptic (kills germs) and analgesic (pain killer). It also reduces swelling.
Preparation: The sassafras root is boiled in order to extract its oil. Oil is lighter than water, so it will separate. Then one can remove the oil from the water and apply it to the blisters in order to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and kill germs.
Active Chemical Ingredient: Safrole
Chemical Structure:

Resources:
Safrole. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/safrole#section=Top
Medical Attributes of Sassafras albidum - sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://klemow.wilkes.edu/Sassafras.html
Sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/sassafras
Sassafras albidum - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/sassafras-albidum.html
Ayers, C. (n.d.). How to Extract Sassafras Oil. Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.ehow.com/how_7766393_extract-sassafras-oil.html
Resources:
Safrole. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/safrole#section=TopMedical Attributes of Sassafras albidum - sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://klemow.wilkes.edu/Sassafras.html
Sassafras. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://mdc.mo.gov/discover-nature/field-guide/sassafras
Sassafras albidum - Natural medicine facts. (n.d.). Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.naturalmedicinefacts.info/plant/sassafras-albidum.html
Ayers, C. (n.d.). How to Extract Sassafras Oil. Retrieved September 8, 2015, from http://www.ehow.com/how_7766393_extract-sassafras-oil.html



No comments:
Post a Comment