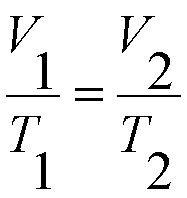- "Gases consist of small particles (molecules) which are in continuous motion
- "The volume of the molecules present is negligible compared to the total volume occupied by the gas"
- "Intermolecular forces are negligible"
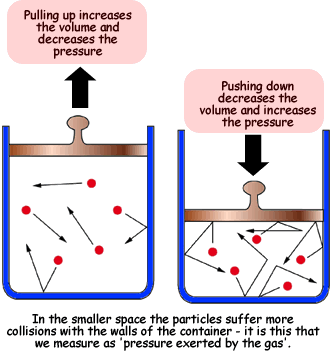
- "Pressure is due to the gas molecules colliding with the walls of the container"
Real gases are different from ideal gases because there is less kinetic energy in real gases at low temperatures. So, they are able to attract each other at high pressures because they are closer together so that the volume of the gas molecules becomes significant compared to the volume the gas occupies.
Below is the formula used for the Ideal Gas Law:
 |
| http://dl.clackamas.edu/ch105/lesson1ideal_gas_law.html |
P=pressure, V=volume, n=moles, R= gas constant, T= temperature. The gas constant in 0.0821 L atm/ mol K
Here is a link that explains ideal gases more:
Ideal Gas Law